Article II 3/2025 - UTILISATION AND PROCESSING OF FISH BY-PRODUCTS IN BANGLADESH: VALUABLE TREASURES, NOT TRASH

However, some by-products can gain added value through further processing and be converted into marketable new products known as coproducts. Fishmeal (made from fish heads, tails, fins and discarded whole fishes not used for human consumption); fish oil (viscera, intestines and gill rakes are used as raw materials); gelatin and collagen (from fish scales, skins and bone frames), chitin and chitosan (crustacean shell wastes) are examples of such co-products.
1 Islam, M.J., and Omar, R.P., 2021. Seafood Waste Management Status in Bangladesh and Potential for Silage Production. Sustainability 2021, 13(4), 2372; https://www.mdpi.com/2071-1050/13/4/2372
2 Islam, J., Yap, E.E.S., Krongpong, L., Toppe, J. and Peñarubia, O.R. 2021. Fish waste management – An assessment of the potential production and utilization of fish silage in Bangladesh, Philippines and Thailand. FAO Fisheries and Aquaculture Circular No. 1216. Rome. https://doi. org/10.4060/cb3694en
3 FAO and INFOFISH 2024. Compilation of Value-Added Products with Materials Originated from Aquatic Resources. A study on fish by-products conducted in Bangladesh, Malaysia, Indonesia, Philippines and Thailand. 82 pages (To be published).
Fish scales and skin

Fish skins (derived from Pangasius and other catfish) are also major sources of collagen. Since freshwater fish skins constitute 3–5% of the raw material, Bangladesh has the potential to accumulate approximately 4 000 tonnes (1,438–7,190 tonnes) of skins from freshwater fishes, which is enormous. But the fish skins are usually not collected or processed in the country, becoming waste in the process (Table 1).
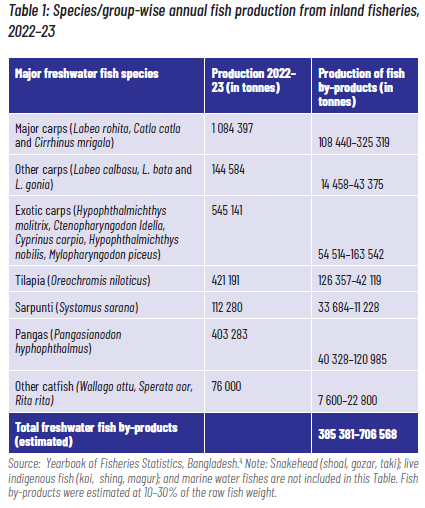
4Yearbook of Fisheries Statistics of Bangladesh 2022-23, Fisheries Resources Survey System, Department of Fisheries, Ministry of Fisheries and Livestock, Govt. of the People’s republic of Bangladesh. Pages 124. 2024-07-08-03-59-c335f1d6908e7427417e8bc610142b63.pdf
Once washed, the wet fish scales are sun-dried (or mechanically with the help of a dryer during rainy days) to maintain the best quality. Dust particles are carefully removed with the help of a sieve and the dried fish scales (a valuable and natural source of collagen) are packed in 25 kg or 50 kg sacks and finally shipped by exporters to international markets. Details on the processing and utilization of fish scales in Bangladesh can be found here and here.
Pituitary glands
After collecting, the PGs are taken to the laboratory for processing which includes cleaning, followed by a dehydration procedure with acetone treatment to preserve and prepare the glands for use (Best practices of PG collection and processing). Finally, the product is dried, weighed, and packaged in bottles designed to meet export quality standards. The unit price of PGs varies from Tk 4-6 (USD 0.03-0.45) to Tk 10 -15 (USD 0.08-0.012) during the wet and dry stages respectively, and between USD 10 to USD 100 per gram of final product, depending on their quality, size and eficacy.

Shrimp shells
Optimising this IMTA peatland approach demands strategic design and effective management, including spatial arrangement for waste to disperse towards algal and aquatic plant (duckweed) growth areas, promoting interspecies relationships throughout the entire site [10]. Spatial design also involves the strategic placing of species in proximity to each other, such as filter feeders adjacent to fish to use waste nutrients. The roles of subject-matter experts on site is crucial, such as environmental (civil) wastewater engineers; this ensures effective managing of water and waste flow for facilitating nutrient exchange and maintaining optimised growth conditions for all trophic species. This includes creating the best conditions for natural filtration capabilities of certain trophic species. Moreover, the site should exhibit stable hydrology, appropriate pH levels, and minimal pollution to support these diverse aquaculture species.
This IMTA process will contribute to restoring degraded peatlands into their natural state, thus facilitating carbon sequestration and an ecological balance that also mitigates against the use of unwanted chemicals [15]. Other successful examples of IMTA systems have been reported globally, such as fish farming in combination with reed bed filtration systems in the United Kingdom [17]; integrating shrimp farming with mangrove restoration in Indonesia that reduces erosion and augments carbon sequestration [18]; and combining salmon farming with seaweed and mussel cultivation in Canada’s Atlantic region [19] to improve nutrient recycling and environmental impact.
The Irish government has taken steps towards turning Ireland into a global bioeconomy leader, promoting access to Mount Lucas as a national demonstration site for aquaculture and aquatech with a linked bioeconomy theme [1]. The strategic policies in Ireland that have global relevance include boosting employment and new business opportunities in rural, regional, urban, and coastal areas through innovation products, services and technologies; increasing food and energy security; supporting climate action by displacing fossil fuels; promoting a circular economy and reducing waste; providing high-value diversification opportunities for transforming agrifood systems; and leveraging research, development and innovation capabilities to address bioeconomy, societal and environmental challenges [20). The pivotal role of integrated demonstration facilities in developing tangible biobased opportunities at scale (including digital transformation) has yet be described [16, 21].
Defining a circular IMTA in the peatlands for production of trout, microalgae and macroalgae biomass provides an excellent example of a tangible “in action model” that can be replicated globally [15]. The mortality on site in the production of trout in Irish peatlands is very low [1]; however, the site is exposed to the elements where it has experienced significant challenges in managing the effects of successive storms and variance in weathering. Thus, this site also enabled modelling and prediction as to the impact of changing weather events and patterns on open food ecosystems, to both understand and mitigate against the impact of climate change [15].
The IMTA site will be connected fully to digital sensors to facilitate the optimal reuse of waste and sludge. In addition, there will be an onsite extended reality suite that enables 360° visualisation of the site operation, including the remote development of bespoke aquatech innovation. Such a defined IMTA system is in sync with the environment where profiling of different tropic levels enables eco-labelling (green) for new products that are compliant with ecology and with nature. The IMTA site at Mount Lucas does not rely on the use of pesticides or antibiotics, nor the complex use of physical technologies for end-of-pipe solutions for treating efluent. Developing such IMTA sites in the peatlands creates new exciting opportunities in terms of usage, while educating our next generation of change-makers for a cleaner resource-eficient world.

In Bangladesh, export data on fish scales and shrimp shells are combined under the same HS Code category, presenting a challenge to quantify them separately. The export of fish scales and shrimp shells was recorded at 1 881.28 tonnes worth USD 1 822 641.59 in 2020–2021. In the following year, the export of shrimp shells was recorded as 3 022.62 tonnes, valued at USD 3 658 425. There is no doubt that if the Department of Fisheries were to take the initiative to collect, process and utilise shrimp and other crustacean shells in the country, it would benefit the sector economically and reduce environmental pollution in the long run.
Currently, a significant amount of shrimp shells and appendages (both spoiled and fresh) are collected by local contractors. After that comes the sorting out of unwanted particles and packing in 25kg or 50kg sacks; and finally, the finished packs are exported to China, Republic of Korea, Thailand and Indonesia as raw materials for the pharmaceutical and cosmetic industry. (Shrimp by-product utilization in Bangladesh). Lastly, the spoiled shrimp shells go for landfilling. A targeted processing, utilisation and value chain development plan for the industry in Bangladesh can result in substantial economic returns for these by-products.
The price of each kg of shrimp shells varies from Tk 2–5 to Tk 5–10 (USD 0.016–0.041 to 0.041–0.082) during the wet and dry stages respectively. Export price uctuations may also occur depending on the quality, presence of dust particles and moisture content of the shells. Comparatively, the export price of ¬sh scales is between USD 700–1400 per tonne, depending on the species, size and quality of the raw material.
Fish maws

6 Xing et al., 2025. Species authentication and conservation challenges in Chinese fish maw market using Mini-DNA barcoding. Food Control. Volume 167, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont. 2024.110779
Generally, fish maws are collected by fish dressers at the local wet markets. They are cleaned thoroughly with freshwater and sun-dried by using various techniques and finally packed for export. These byproducts are used in popular Chinese dishes like fish maw soups and fish maw stews. They are also used to produce high-value surgical sutures in addition to being a good source of collagen and fibre. The key steps in the collection, processing and utilisation of the fish maws from wet market to exporter level in Bangladesh are outlined here. (Best practices for collection and processing of fish maws in Bangladesh)
Dried fish maw is a lucrative fishery commodity; for instance, one kilogram of swim bladders from Johinus coiter, locally known as Datina koral, and white grunter (Pomadasys hasta), sold for BDT 400 000–500 000 (USD 3 404–4 256) during the study period. Similarly, the swim bladders from Indian salmon also commanded high prices, selling at BDT 100 000 per kg (USD 851). Pike eel (Muraenesox bagio) swim bladders sold for BDT 25 000–40 000 per kg, whereas those from eel, rui (Labeo rohita), pangasius (Pangasius hypophthalmus), catla (Catla catla), boal-catfish (Wallago attu), lakkha (Leptomelanosoma indicum), lambo (Joe-fish) and other whitefish sold at BDT 5 000–6 000 per kg (USD 43–52).
The export of fish maws and fins from Bangladesh to countries such as China (including Hong Kong SAR), United Arab Emirates and Vietnam has gained momentum, driven by the high demand for these products.
Fishmeal and fish oil
There is no oficial record of fishmeal and fish oil production in Bangladesh. According to a study by WorldFish/USAID, about 1 million tonnes of commercial feed and 0.3–0.4 million tonnes of farm-made feed were produced in 2012. Currently, the commercial pellet feed production in the country is estimated at about 1.6 million tonnes per year, while the amount of farm-made feed has reduced drastically due to the introduction of extruded feed (floating feed). Almost all the fishmeal and fish oil required to produce fish feed is imported. Considering the inclusion of fishmeal and fish oil at 10kg and 1 litre respectively in the manufacture of commercial feed per tonne, the demand for fishmeal and fish oil is approximately 16 000 tonnes and 16 000 litres per year, which is huge. By converting local fish by-products into valuable fishmeal and fish oil, imports can be reduced. Moreover, the fish oil can be used in various sectors such as nutraceuticals, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics and animal feeds.
7 Improving Aquaculture Feed in Bangladesh: From Feed Ingredients to Farmer Profit to Safe Consumption. An article published in The Fish Site.com. https://thefishsite.com/articles/improvingaquaculture- feed-in-bangladesh-from-feed-ingredients-to-farmer-profit-to-safe-consumption.

Sharks and rays
Major challenges and recommendations
- The stakeholders involved in the fish scale value and supply chain are still using traditional collection and processing methods.
- There is a lack of competitiveness in the domestic market and access to potential export markets.
- Dearth of knowledge and information at the competent authority level and among other stakeholders regarding the gathering of data on fish by-products and their utilisation.
- No/limited capacity building or training conducted by the relevant agencies to manage, utilise and process the fish byproducts, with only the private sector being aware of the market potential.
- Huge amounts of shrimp and crab shells constitute a public nuisance and cause environmental pollution especially during the peak season when they are discarded in landfills.
- Inadequate financial support for young and new entrepreneurs; as well as insuficient facilities to further process fish byproducts into co-products.
- Limited or no R&D activities to improve processing and utilisation.
- A lack of a national conservation strategy and plan of action for endangered sharks and rays in Bangladesh to protect them from extinction.
The following recommendations are highlighted to address the above challenges:
- The country needs cutting-edge technologies and improved processing facilities to enhance eficiency and quality, product innovation and better utilisation of by-products.
- The country needs cutting-edge technologies and improved processing facilities to enhance eficiency and quality, product innovation and better utilisation of by-products.
- Training and capacity-building for industry stakeholders should be emphasised to realise the full potential of the by-product value chains and to facilitate trade and market access.
- More financial assistance is necessary to spearhead innovative technologies, including greater access to interest-free loans to improve processing facilities.
- Initiate more R&D and Innovative projects to strengthen publicprivate partnerships.
- Formulate a national conservation strategy and plan of actions for sharks and rays; and implement the existing laws aimed at species and fisheries biodiversity conservation.
Conclusion
























